Just as with Blueprints the entire BrainCloud API is available through C++ in Unreal. In this tutorial we will go over how to Initialize brainCloud, how to Authenticate, and how to use the callback system.
Prerequisites
- Created a brainCloud Portal account
- Created a game in the brainCloud Portal. If you need help with this step refer to the Unity Tutorial #1 video.
- An Unreal project with the brainCloud plugin installed as described here
- Basic experience with Unreal C++, see the Unreal documentation for help
Creating a Test Actor
For this tutorial we will need to create an actor where we will write our code to interact with brainCloud. To create a new actor open the editor and go to File>New C++ Class. Select Actor as the parent class, click Next, and name it whatever you like.
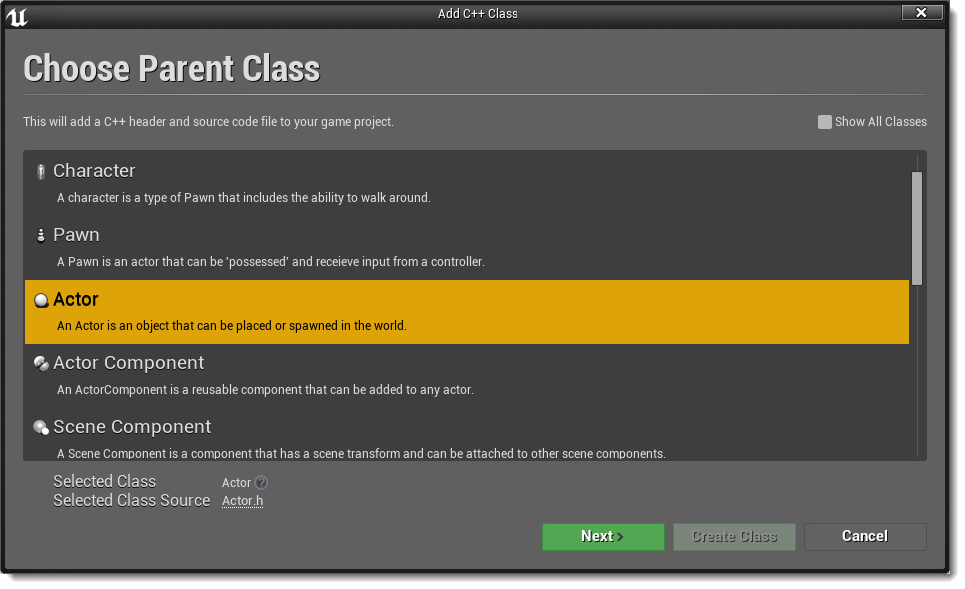
One your actor is created switch over to your programming IDE and continue the tutorial from there.
Including the BCClientPlugin Module
The BCClientPluginModule must be added to your Project’s Build.cs file for the Unreal Build Tool to successfully compile your project with brainCloud. Find the Build.cs file under Source > MyProject > MyProject.Build.cs
Inside the Build.cs find the line PublicDependencyModuleNames and add the string “BCClientPlugin” to it. It should now look something like this:
PublicDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(new string[] { "Core", "CoreUObject", "Engine", "InputCore", "BCClientPlugin" });
Initialization
Before you can do anything with brainCloud the BrainCloudClient must be initialized. This is accomplished by providing your App’s details to the Client via the Initialize function.
Open your newly created Actor’s code (cpp) file and include the “BrainCloudClient.h” header file. This will give you access to all of brainCloud’s services and functions.
#include "BrainCloudClient.h"Now in your actor’s BeginPlay() function we can perform the initialization using the BrainCloudClient->Initialize function.
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
void ABrainCloudTestActor::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
_bc.initialize(
"https://sharedprod.braincloudservers.com/dispatcherv2",
"91c3a097-4697-4787-ba1c-fakeSecret",
"123456",
"1.0.0");
}
Updating the BrainCloud Client
The BrainCloudClient relies on its Run Callbacks function being called every frame from the main thread, without this your callback functions will never be called! There are many places you could call this function, but to keep things simple in this tutorial we will place it in our actor’s Tick() method.
// Called every frame
void ABrainCloudTestActor::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
_bc.runCallbacks();
}
Setting Up Callbacks
Before we make any API calls we want our actor to be able to receive callbacks from brainCloud when our API calls succeed or fail. To do this we need our actor to inherit from the IServerCallback class. This interface defines the serverCallback and serverError functions, and allows us to pass a reference to our actor as a callback object to brainCloud.
Go to your actor’s header file and include the IServerCallback.h header file. Next, inherit from IServerCallback and declare the virtual methods required by the interface. Your header should look similar to this:
#pragma once
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "IServerCallback.h"
#include "BrainCloudTestActor.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class MYPROJECT_API ABrainCloudTestActor : public AActor, public IServerCallback
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
ABrainCloudTestActor();
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick( float DeltaSeconds ) override;
// IServerCallback interface
void serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData);
void serverError(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, int32 statusCode, int32 reasonCode, const FString& jsonError);
// End of IServerCallback interface
};
The next step is to go back to your cpp file and define the serverCallback and serverError methods like so:
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData)
{
}
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverError(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, int32 statusCode, int32 reasonCode, const FString& jsonError)
{
}
And add the required header files for ServiceName and ServiceOperation which we will use later.
#include "ServiceName.h" #include "ServiceOperation.h"
Authentication
BrainCloud provides many different methods of authentication, but for this tutorial we will use AuthenticateUniversal. Now that our actor can receive callbacks we can proceed to call the AuthenticateUniversal method after we initialize in BeginPlay().
_bc.getAuthenticationService()->authenticateUniversal("UnrealUser", "password1234", true, this);
Referring to the documentation, the last parameter of the AuthenticateUniversal function is a pointer to an IServerCallback. Since our actor has inherited from IServerCallback we can pass in the this pointer and have our actor’s serverCallback and serverError functions get called when the server responds to our request.
Let’s add a log message to our serverCallback method so we know things are working.
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Authenticated!"));
}
At this point, you should be able to run the Editor, drag your Actor into the Level, press Play, and see “LogTemp:Display: Authenticated!” in the Output Log window.
Parsing JSON
All brainCloud callbacks include a JSON data string as a parameter where the return data for the call is represented. Being able to parse this string is essential to using brainCloud, so this section of the tutorial goes over how to use the built-in Unreal JSON classes with the brainCloud JSON data.
The first thing we need to do is add the Unreal Json module to our project’s Build.cs file so we can use the JSON functionality. The Build.cs file should be under Source > MyProject > MyProject.Build.cs
Inside the Build.cs find the line PrivateDependencyModuleNames and add the string “Json” to it. It should look something like this:
PrivateDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(new string[] { "Json" });
Back in our Actor’s cpp file, lets modify the serverCallback to send another call after AuthenticateUniversal returns, and then to handle the return of this additional call as well.
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData)
{
if (serviceName == ServiceName::AuthenticateV2) //authenticate return handling
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Authenticated!"));
//send our next request
_bc.getTimeService()->readServerTime(this);
}
else if (serviceName == ServiceName::Time) //time return handling
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Reading the time..."));
}
}
Because we’re passing in a pointer to our Actor for our next call as well we need to check which call is invoking our serverCallback function. We can do this by comparing the ServiceName and acting accordingly.
We’ve also added our next API call ReadServerTime which as the documentation says “returns the server time in UTC. This is in UNIX millis time format.” Now lets process the return JSON string to get the time and print it to the log.
First thing we need to do is create a new TJsonReader to read our JSON string, and a FJsonObject to hold our deserialized data.
TSharedRef<TJsonReader<>> reader = TJsonReaderFactory<>::Create(*jsonData); TSharedPtr<FJsonObject> jsonReadObject;
Now we actually deserialize the string using the FJsonSerializer::Deserialize method and passing in our JsonReader and JsonObject.
bool result = FJsonSerializer::Deserialize(reader, jsonReadObject);
We check the result bool returned by the Deserialize to make sure it was successful before digging into our jsonReadObject for the data we need.
Referring to the JSON return structure in the documentation we can see that the server time is represented by the key “server_time” which is contained in the object “data”. So to get to it we take the jsonReadObject and use the functions GetObjectField and then GetNumberField, passing in “data” and “server_time” as our Field Names.
Finally we print the extracted time to the log.
if (result == true) //if deserializing was successful
{
TSharedPtr<FJsonObject> data = jsonReadObject->GetObjectField(TEXT("data"));
int64 serverTime = data->GetNumberField(TEXT("server_time"));
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("The time is %d"), serverTime);
}
Full Source Code
Header:
#pragma once
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "IServerCallback.h"
#include "BrainCloudTestActor.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class BCSUBSYSTEM_API ABrainCloudTestActor : public AActor, public IServerCallback
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
ABrainCloudTestActor();
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick( float DeltaSeconds ) override;
// IServerCallback interface
void serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData);
void serverError(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, int32 statusCode, int32 reasonCode, const FString& jsonError);
// End of IServerCallback interface
};
Source:
#include "MyProject.h"
#include "BrainCloudTestActor.h"
#include "BrainCloudClient.h"
#include "ServiceName.h"
#include "ServiceOperation.h"
BrainCloudClient _bc;
// Sets default values
ABrainCloudTestActor::ABrainCloudTestActor()
{
// Set this actor to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it.
PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = true;
}
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
void ABrainCloudTestActor::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
_bc.initialize(
"https://sharedprod.braincloudservers.com/dispatcherv2",
"91c3a097-4697-4787-ba1c-fakeSecret",
"123456",
"1.0.0");
_bc.getAuthenticationService()->authenticateUniversal("UnrealUser", "UnrealUser", true, this);
}
// Called every frame
void ABrainCloudTestActor::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
_bc.runCallbacks();
}
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverCallback(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, const FString& jsonData)
{
if (serviceName == ServiceName::AuthenticateV2) //authenticate return handling
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Authenticated!"));
//send our next request
_bc.getTimeService()->readServerTime(this);
}
else if (serviceName == ServiceName::Time) //time return handling
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Reading the time..."));
TSharedRef<TJsonReader<>> reader = TJsonReaderFactory<>::Create(*jsonData);
TSharedPtr<FJsonObject> jsonReadObject;
bool result = FJsonSerializer::Deserialize(reader, jsonReadObject);
if (result == true) //if deserializing was successful
{
TSharedPtr<FJsonObject> data = jsonReadObject->GetObjectField(TEXT("data"));
int64 serverTime = data->GetNumberField(TEXT("server_time"));
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("The time is %d"), serverTime);
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to deserialize JSON!"));
}
}
}
void ABrainCloudTestActor::serverError(ServiceName serviceName, ServiceOperation serviceOperation, int32 statusCode, int32 reasonCode, const FString& jsonError)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Call failed - %s - %s"), *serviceName.getValue(), *serviceOperation.getValue());
}
